Hearing loss is a broad term that covers different degrees of reduced hearing ability. This condition can be caused by many different factors—some temporary, some long-lasting, and others difficult to reverse. In today’s world hearing problems are becoming more common, as people are exposed to loud environments, stress, constant use of technology, and unhealthy lifestyles.
Hearing loss affects daily life in many ways. For some people it begins as a mild difficulty noticing certain sounds, but over time it can progress to the point where normal conversations become hard to follow. This can create serious challenges at work, where communication and quick response are essential. Hearing impairment can also be dangerous: while walking down the street, a person might not hear a car horn, a warning signal, or an alarm at home.
The causes of hearing loss are diverse. Doctors point to infectious diseases and their complications, neuritis of the auditory nerve, toxic effects from certain medications, disruption of normal blood circulation in the ear, fluctuations in blood pressure, and various kinds of injuries — including head trauma and direct damage to the ear. Prolonged exposure to loud noise or vibration is another major cause, especially among people working in industrial or construction environments.
Still, one of the most common reasons for hearing loss is aging. Over time, the delicate hair cells inside the inner ear, which are responsible for translating sound waves into nerve signals, begin to break down. This is why many older adults experience problems with hearing. However, today hearing difficulty is becoming increasingly common even among young people, due to constant noise exposure, long-term headphone use, stress, and the heavy influence of modern technology.
The gradual decline of hearing often leads to social discomfort. People become quieter, speak less in conversations, and frequently ask others to repeat themselves. This can cause embarrassment and, in some cases, even social withdrawal. Psychologically, hearing loss increases fatigue because the brain tries harder to decode unclear sounds. Some people even believe others are speaking more quietly or mumbling, without realizing the issue lies within their own hearing.
Natural remedies, while they cannot replace medical treatment, are sometimes used as complementary methods. Garlic is one of the most widely known natural remedies, valued not only as a culinary ingredient but also for its strong medicinal properties. Rich in antioxidants and known for its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial qualities, garlic has been used for centuries in traditional medicine for respiratory problems, immune support, and general inflammation.
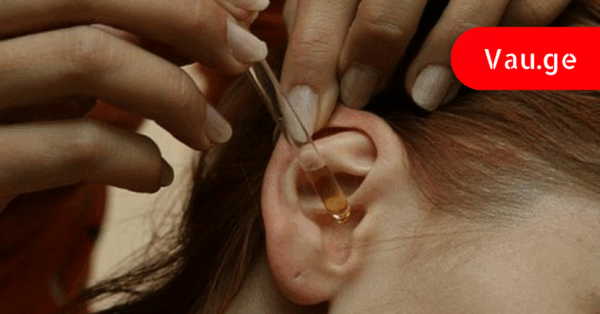
There is a traditional belief that a mixture of garlic juice and olive oil can provide some relief when applied to the ear. According to folk practice, this mixture may help with mild discomfort, dryness, or irritation around the ear area. It is important to note that such remedies do not replace medical advice and are not considered official treatments, but many people use them as gentle supportive care.
To prepare the mixture, you need three cloves of garlic, a small amount of olive oil, cotton, and a dropper bottle. The garlic is washed, peeled, and squeezed to extract as much juice as possible. The juice is then mixed with olive oil and poured into a dropper. According to traditional use, 3–4 drops are placed into the ear, after which the ear is covered with cotton, and the person is advised to lie down for a short while to allow the mixture to settle. Many people report a warm, comforting sensation in the ear area after using this method.
However, doctors emphasize that symptoms such as ear pain, ringing, sudden hearing loss, or dizziness require immediate medical attention. Self-treatment in such cases is not recommended. Natural remedies can be used as mild supportive methods, but they cannot diagnose or treat medical conditions.
There are many safe and effective ways to care for your hearing: avoiding loud environments, using headphones at no more than 60% volume, avoiding the insertion of foreign objects into the ears, treating infections early, monitoring blood pressure, and scheduling regular check-ups with a specialist. Nutrition also plays a role — vitamins from the B-group, zinc, magnesium, and antioxidants support overall nerve function and circulation.
Folk remedies, including the use of garlic and oil mixtures, may bring comfort to some people, but should be used with caution and awareness. Only a medical professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan. It is important to understand that hearing health is just as significant as vision or heart health. Protecting your hearing begins with daily care, creating a safe environment, and seeking professional guidance when needed.