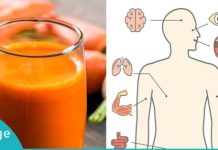
Arterial hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a major risk factor for the development of cardiovascular diseases, stroke, kidney disorders, and vascular complications. It affects the heart, brain, kidneys, and blood vessels, and if left unmanaged, can lead to serious long-term health issues. While hypertension can occur at any age, it is most frequently diagnosed in people over 50 years old. It is relatively rare in individuals under 30, although genetic predispositions and lifestyle factors can occasionally lead to early onset.

High blood pressure places a continuous strain on the walls of blood vessels and the heart, increasing the risk of heart attack, aneurysms, chronic kidney disease, and other complications. Because the disease often progresses silently, it is frequently referred to as the “silent killer,” emphasizing the importance of regular monitoring and preventive care, particularly for older adults.
Causes and Risk Factors
The precise causes of hypertension are not fully established, but it is generally understood to result from a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental or lifestyle factors. Key contributors include:
Genetic Predisposition: Family history significantly increases the likelihood of developing hypertension.
Excess Body Weight: Overweight and obesity place additional stress on the cardiovascular system, making blood pressure regulation more difficult.
Chronic Stress: Prolonged mental and emotional stress can elevate blood pressure by triggering sustained activation of the sympathetic nervous system.
High Salt Intake: Excessive consumption of table salt contributes to fluid retention and increased vascular resistance.
Alcohol and Tobacco: Both alcohol and cigarette use can elevate blood pressure and damage blood vessels over time.
Diabetes Mellitus: High blood sugar levels contribute to vascular damage and increase the risk of hypertension.
High Cholesterol Levels: Elevated cholesterol can lead to atherosclerosis, further impairing blood flow and raising blood pressure.
Other contributing factors may include a sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, and aging, all of which can exacerbate the risk of developing hypertension.
Nutritional Recommendations for Hypertension
For individuals with hypertension, diet plays a crucial role in managing blood pressure levels. A heart-healthy diet should focus on:
Fruits and Vegetables: These provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that help maintain vascular health.
Magnesium, Calcium, and Potassium-Rich Foods: These minerals support normal blood pressure regulation. Foods such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and dairy are recommended.
Low-Fat Dairy Products: Yogurt, milk, and cheese with reduced fat content can provide calcium and protein without excessive saturated fats.
Healthy Fats: Plant-based oils, avocados, and nuts are preferable to saturated and trans fats.
Fluid Balance: Monitoring daily fluid intake and output can help prevent edema and maintain optimal blood pressure.
Regular Physical Activity: Even moderate activity, such as daily walks for at least 30 minutes, supports cardiovascular health and weight management.
Weight Control: Maintaining a healthy body weight reduces the strain on the heart and blood vessels, lowering the risk of hypertension-related complications.
An Effective Natural Remedy: Caraway Seed Infusion
For those seeking a natural approach to managing high blood pressure, caraway seeds provide a time-tested remedy. When prepared correctly, this simple infusion can help normalize blood pressure, relieve constipation, alleviate stomach and bladder discomfort, and support urinary and digestive health.
Preparation Instructions:
Take 1 tablespoon of caraway seeds and place them in a teapot.
Pour 0.5 liters of boiling water over the seeds.
Cover the teapot with a cloth or wrap it in a towel for 40 minutes, ensuring the seeds remain in the steam and all the valuable nutrients are retained in the water.
The resulting infusion should be consumed directly from the teapot. Drink three sips at a time, seven to ten times daily, preferably with meals, not on an empty stomach or immediately after eating. The recommended treatment course is one week, after which the infusion can be used periodically for maintenance, for example, 2–3 days per month as a preventive measure.
Benefits of Caraway Seed Infusion
Beyond its effectiveness in normalizing blood pressure, caraway seed infusion provides a wide range of additional health benefits:
Respiratory Health: The infusion can help alleviate coughing, bronchitis, and sore throat symptoms.
Digestive Support: It promotes healthy digestion, reduces bloating, and relieves constipation.
Urinary Health: It supports bladder function and can help reduce discomfort associated with urinary issues.
Sleep Quality: Regular consumption may improve sleep patterns and help combat insomnia.
Overall Wellness: Caraway seeds are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support general health and vitality.
The natural properties of caraway seeds, including their anti-inflammatory, diuretic, and mild sedative effects, make this infusion a versatile and safe home remedy when used according to the instructions.
Additional Recommendations
While caraway seed infusion is highly effective, it should be complemented with lifestyle adjustments to maximize benefits:
Balanced Diet: Continue consuming fresh fruits, vegetables, and mineral-rich foods.
Moderate Exercise: Daily physical activity supports cardiovascular function and helps maintain optimal blood pressure.
Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga can help reduce stress-induced blood pressure spikes.
Regular Monitoring: Check blood pressure at home or with a healthcare professional to track progress and detect potential issues early.
Avoid Excess Salt, Alcohol, and Tobacco: These factors can negate the benefits of the infusion and exacerbate hypertension.
Conclusion
Arterial hypertension is a common and serious condition, particularly among individuals over 50. Genetic predisposition combined with lifestyle and dietary factors can lead to elevated blood pressure, which in turn increases the risk of heart, kidney, and vascular diseases. While conventional medications are available, natural remedies such as caraway seed infusion provide a safe, effective, and inexpensive alternative.
When prepared and consumed properly, caraway infusion can normalize blood pressure, relieve digestive and urinary discomfort, improve sleep, and support overall health. Combined with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, this simple home remedy can be a cornerstone of natural hypertension management. By incorporating these practices into daily life, individuals can achieve long-term cardiovascular health and improved well-being without relying solely on expensive medications.