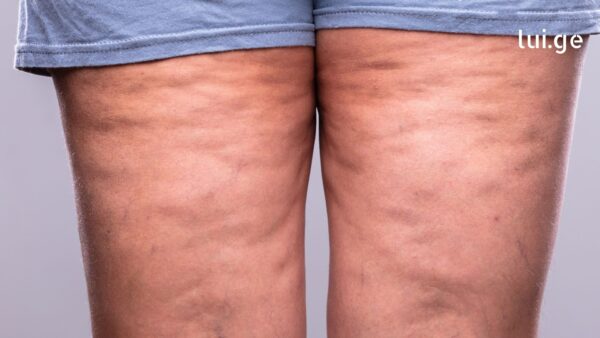
Did you know that constant fatigue, a feeling of heaviness, or swelling in your arms and legs might not be simple tiredness, but a clear signal from your body that it’s retaining too much fluid?
Fluid retention, medically known as edema, is one of the most common issues people face, often without even realizing it. This condition occurs when excess fluid builds up in your body’s tissues, particularly under the skin or within body cavities.
While it may seem like a minor inconvenience at first, persistent water retention can indicate underlying health problems that should not be ignored. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the causes, symptoms, and most effective ways to deal with fluid retention naturally—without relying on harsh medications.
What is Fluid Retention and Why Does It Happen?
Fluid retention is essentially your body holding on to water instead of flushing it out properly. Normally, your kidneys maintain the perfect fluid balance by removing excess water through urine. However, when this system is disrupted, water starts pooling in the tissues.
This issue is not just about aesthetics (like puffy ankles or a bloated belly); it can signal something more serious, such as:
Poor blood circulation
Lymphatic system disorders
Hormonal imbalances
Kidney or liver issues
Women often experience it during PMS, pregnancy, or menopause, while men might notice it due to poor diet or lack of physical activity.
Where Does Fluid Accumulate?
Although it can affect almost any part of the body, fluid retention commonly targets:
Legs and ankles – Swollen feet at the end of the day? Classic sign.
Hands and arms – Rings feeling tighter than usual? Another indicator.
Face and eyelids – Puffy eyes in the morning often hint at fluid buildup.
Abdomen – That stubborn belly bloating might not just be from food.
Key Symptoms of Fluid Retention You Should Never Ignore
Many people confuse water retention with simple weight gain, but the symptoms are quite specific. Here are the top warning signs your body is holding onto excess fluid:
1. Noticeable Swelling in Limbs
One of the clearest signs is swelling in the legs, ankles, feet, or hands. This swelling often becomes more visible after long periods of sitting or standing. It happens because poor blood flow and increased pressure in the veins cause fluid to leak into surrounding tissues.
Other areas that can swell include:
Stomach (abdominal bloating)
Chest area
Face, especially around the eyes
2. Persistent Feeling of Heaviness
That dragging sensation in your legs after a normal day might not be fatigue—it’s your body struggling with excess water weight. Fluid retention increases overall body mass, adding stress to your muscles, lymphatic system, and blood vessels, which can lead to discomfort and poor circulation.
3. Worsening Cellulite
Cellulite is influenced by many factors, but fluid retention can make it look worse and harder to treat. The excess water accumulates in fat cells, creating a more uneven and noticeable appearance on thighs and buttocks.
While massages and cosmetic treatments can reduce its visibility, the only real solution is addressing the root cause—excess fluid buildup.
4. Unexplained Fatigue and Weakness
When your body retains too much fluid, it affects circulation. Cells receive less oxygen and fewer nutrients, leaving you feeling constantly tired, mentally foggy, and physically weak. If you’ve been experiencing low energy for no apparent reason, water retention could be the culprit.
5. Reduced Urination
Another tell-tale sign: you’re drinking water, but you’re not urinating as often as usual. This indicates your kidneys aren’t filtering properly, allowing fluid to accumulate. Reduced urine output also increases the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs).
Top Causes of Fluid Retention
Understanding why it happens is the first step toward fixing it. Common causes include:
High salt intake – Too much sodium traps water in tissues.
Sedentary lifestyle – Lack of movement slows circulation.
Hormonal fluctuations – Common during PMS or menopause.
Certain medications – Steroids, antihypertensives, and others.
Underlying health conditions – Heart, kidney, or liver disorders.
How to Prevent and Reduce Fluid Retention Naturally
Fortunately, you don’t always need prescription diuretics to combat fluid retention. Here are simple, science-backed strategies to restore balance and improve circulation:
✅ 1. Limit Your Salt Intake
Salt is the #1 enemy when it comes to fluid retention. Excess sodium causes your body to cling to water like a sponge. The solution?
Cut down on table salt.
Avoid processed foods like sausages, canned meals, aged cheeses, and ready-made snacks.
Skip sugary sodas—they’re loaded with sodium and additives.
✅ 2. Drink More Water
It may sound counterintuitive, but drinking more water helps reduce water retention. When your body senses dehydration, it holds on to water as a survival mechanism. Stay hydrated to flush out toxins and excess sodium.
✅ 3. Add Natural Diuretic Foods to Your Diet
Certain foods act as gentle, natural diuretics, helping your body eliminate excess water without harsh chemicals. Include these in your daily meals:
Pineapple
Artichoke
Beetroot
Watermelon
Melon
Ginger
These foods also supply vitamins and antioxidants that support kidney health.
✅ 4. Avoid Tight Clothing
Tight jeans or compression garments might look stylish, but they impair circulation and worsen swelling. Choose looser, breathable fabrics that allow proper blood flow.
✅ 5. Get Moving
Physical activity is one of the best remedies. Even 20-30 minutes of daily exercise can make a huge difference by:
Boosting circulation
Reducing venous pressure
Promoting lymphatic drainage
Simple activities like walking, swimming, yoga, or cycling work wonders.
Bonus Tips for Quick Relief
Elevate your legs after a long day to encourage fluid drainage.
Massage the swollen areas to stimulate lymphatic flow.
Avoid excessive alcohol and caffeine, which dehydrate and disrupt fluid balance.
When to See a Doctor
If swelling persists for more than a few days, worsens, or comes with symptoms like shortness of breath, chest pain, or severe fatigue, seek medical help immediately. These can be signs of more serious conditions like heart failure or kidney disease.
Final Thoughts
Fluid retention is common, but it’s not something you should ignore. While mild cases can often be managed with lifestyle changes—like a balanced diet, hydration, and regular movement—persistent or severe edema always requires professional attention.
By adopting these simple habits, you’ll not only reduce swelling but also improve your overall health, energy levels, and quality of life.
✅ Pro tip: Start with one change today—like reducing salt or adding diuretic foods—and notice how much better you feel within a week.