This is one of the most powerful medicinal plants.
Plantain is widely known as a stubborn weed that constantly reappears in gardens and along roads. However, it is also one of the most powerful healing herbs.
The leaves, seeds, and pesvebi of plantain possess various medicinal properties, enabling it to stop bleeding quickly, heal wounds, and disinfect inflammations. Infusions and juice made from the plant help combat coughs and have diuretic, laxative, sweat-inducing, pain-relieving, and calming effects.
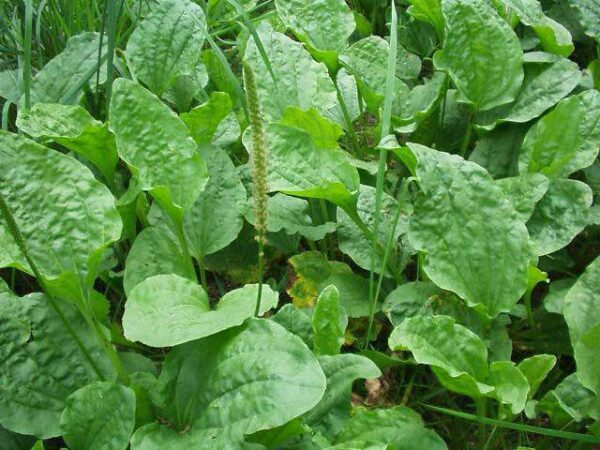

Depending on the ailment being treated, it is best to harvest specific parts of the plant at a time when the concentration of beneficial properties is at its peak.
The leaves, stems, and flowers are most useful after blooming and before seed formation begins. The leaves have a distinctive pattern formed by large veins and are best collected within 60 days of blooming. The seeds become highly medicinal just before full ripening.
The roots of the plant offer the greatest health benefits in autumn—between September and November.
Raw materials for harvesting must be dry. This makes it easier to dry the herbs in a cool, dark place for long-term storage. Do not collect herbs during dew or rain.
Recipe for herbal water infusion:
To prepare an infusion, place 1 tablespoon of chopped herbs into 1 cup of boiling water, let it sit for 30–60 minutes, then strain. This infusion is useful for treating wounds, ulcers, fistulas, and abscesses.
Using plantain for bites, wounds, and bruises:
Fresh leaves have antimicrobial properties and are therefore used for treating burns, slow-healing wounds, infections, ulcers, fistulas, abscesses, and boils. In the case of insect bites, the herb helps stop bleeding faster.
Wash the leaves and apply several layers to the affected area. Replace the leaves every 2–3 hours. You can also use dried leaves—just soak them in warm water before external use.
Medicinal properties of the infusion for coughs:
The infusion stimulates the activity of the respiratory epithelium, promotes the removal of mucus from the bronchi, and has expectorant and cough-suppressing effects. It is used to treat acute respiratory infections, tonsillitis, bronchitis, bronchial asthma, and pulmonary tuberculosis.
To better expel thick mucus during bronchitis, drink half a cup of the infusion 3–4 times daily. In case of colds, a syrup is made by mixing the plant’s juice with an equal amount of honey. Take 1 tablespoon 4 times a day.
Use of plantain for gastrointestinal disorders:
The healing properties of plantain are beneficial for treating gastritis, stomach ulcers, duodenal ulcers, bladder problems, and hemorrhoids.
For home treatment of gastritis, boil 2 teaspoons of plantain seeds in one cup of boiling water, let it sit for 12 hours, and drink it at night. Plantain juice reduces stomach pain, stimulates appetite, increases stomach acidity and secretion, and reduces chronic inflammation in the intestines. Take 1 tablespoon of juice three times a day, 30 minutes before meals.
In warm seasons, it is helpful to eat 10–12 fresh leaves daily (mixed with honey) for gastrointestinal issues. For constipation, take a small amount of dried leaf powder on an empty stomach, washed down with warm water.
Plantain for skin care:
For healing cracked heels, warm baths with plantain infusion are beneficial. A mixture of crushed leaves also helps restore the skin.
Contraindications:
The infusion and juice should not be consumed if you have increased stomach acid. Do not use this herb if you are prone to thrombosis.