Thyroid gland diseases have become increasingly prevalent in today’s modern world. Numerous lifestyle factors and environmental influences contribute significantly to this rising trend. Understanding how the thyroid gland functions and recognizing its symptoms when diseased is vital for maintaining good health.
The Thyroid Gland and Its Importance
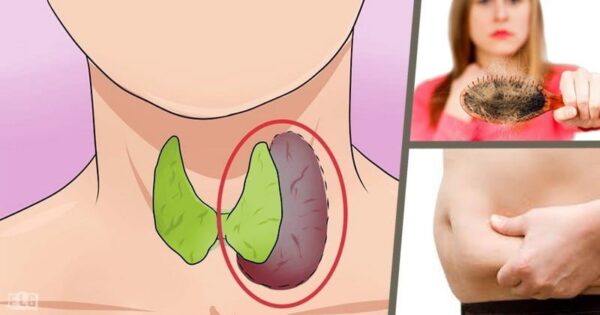
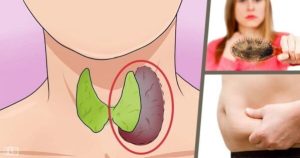
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped organ located in the front of the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. Despite its relatively small size, it has an enormous impact on overall health and well-being. The thyroid produces three primary types of hormones that regulate many physiological processes:
Triiodothyronine (T3)
Thyroxine (T4)
Diiodothyronine (T2)
Among these hormones, about 90% of what the thyroid secretes is T4, which is an inactive form. Our liver then converts T4 into the active hormone T3 with the help of specific enzymes. These hormones regulate metabolism, influence the function of every cell in the body, and affect energy production.
How the Thyroid Functions Normally
When the thyroid gland is healthy and functioning correctly, the levels of T3 and T4 hormones remain balanced within the body. This hormonal balance ensures that the metabolic activity of each cell is properly regulated. However, if the level of T3 becomes insufficient, various negative changes can develop in the body, leading to symptoms of thyroid dysfunction.
Thyroid Disorders: Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism
Disorders of the thyroid gland are primarily characterized by either an excess or deficiency of thyroid hormones, which lead to distinctly different clinical conditions:
Hyperthyroidism
When the thyroid gland becomes overactive and produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the condition is called hyperthyroidism. This leads to an acceleration of many metabolic processes. Common symptoms include:
Rapid heartbeat (palpitations)
Weight loss despite increased appetite
Nervousness or anxiety
Heat intolerance and excessive sweating
Tremors in hands and fingers
Increased bowel movements
Muscle weakness
Enlarged thyroid gland (goiter)
Sleep disturbances
This condition requires timely diagnosis and treatment to avoid serious complications such as heart problems and bone loss.
Hypothyroidism
In contrast, when the thyroid gland is underactive and produces insufficient thyroid hormones, the condition is called hypothyroidism. The body’s metabolism slows down, and symptoms develop gradually. Typical signs of hypothyroidism include:
Fatigue and lack of energy
Depression and low mood
Intolerance to cold temperatures
Dry skin and brittle hair
Weight gain
Hair loss
Sleep apnea
Memory impairments and difficulty concentrating
Hearing impairment
Bradycardia (slow heart rate)
Menstrual irregularities
Constipation
Hoarseness
Muscle weakness and joint pain
Mood swings
Poor appetite
This condition often results from autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto’s disease), iodine deficiency, or thyroid surgery and requires hormone replacement therapy for management.
The Challenge of Treatment
Treating thyroid disorders, particularly hypothyroidism, can be complex. Achieving the right balance in thyroid hormone replacement therapy is essential but sometimes difficult. The goal is to perfectly match the body’s physiological needs, ensuring all tissues receive the appropriate amount of hormones for normal function.
Frequent monitoring of thyroid hormone levels and symptoms helps adjust medication dosages effectively. Patients must work closely with healthcare providers to maintain optimal thyroid status.
The Impact of Thyroid Health on the Body
Because the thyroid gland regulates the metabolism of every cell, its dysfunction can affect multiple body systems. From cardiovascular health and cognitive function to skin condition and reproductive health, thyroid disorders influence many aspects of life. This makes awareness and early detection extremely important.
If left untreated, thyroid diseases can cause serious health problems such as heart disease, infertility, developmental delays in children, and increased risk of other autoimmune disorders.
Conclusion
The thyroid gland may be small, but it exerts a tremendous influence over overall health and well-being. Its diseases, both hypo- and hyperthyroidism, are common and deserve attention from individuals and healthcare providers alike.
If you experience any symptoms suggestive of thyroid dysfunction, it is important to seek medical advice. Timely diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and regular follow-up are the cornerstones of managing thyroid diseases successfully.
About Lui.ge
Lui.ge is a platform dedicated to providing valuable advice on health, personal care, and everyday activities. Our mission is to offer information about natural remedies and recipes that can help you improve your health, enhance your beauty, and simplify daily chores. Most importantly, all of this can be done at home, allowing you to enjoy the process while saving a significant amount of money.
The information you gain from our site can easily become a part of your daily routine. Sharing your experiences with family and friends helps spread useful knowledge and makes life easier for more people.
Lui.ge aims to show that expensive procedures or products are not necessary to be healthy, beautiful, and excellent homemakers. With simple ingredients found in everyone’s kitchen or garden, you can achieve remarkable results right at home.
Please remember that recipes and advice published on Lui.ge are generally safe and beneficial for health. However, it is always advisable to consult a healthcare professional before using any therapeutic recipe, especially if you have ongoing health issues.